Centos6.x 环境中 Mysql 5.7 的安装与简单测试
准备工作:
mysql5.7 下载地址: https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/5.7.html#downloads
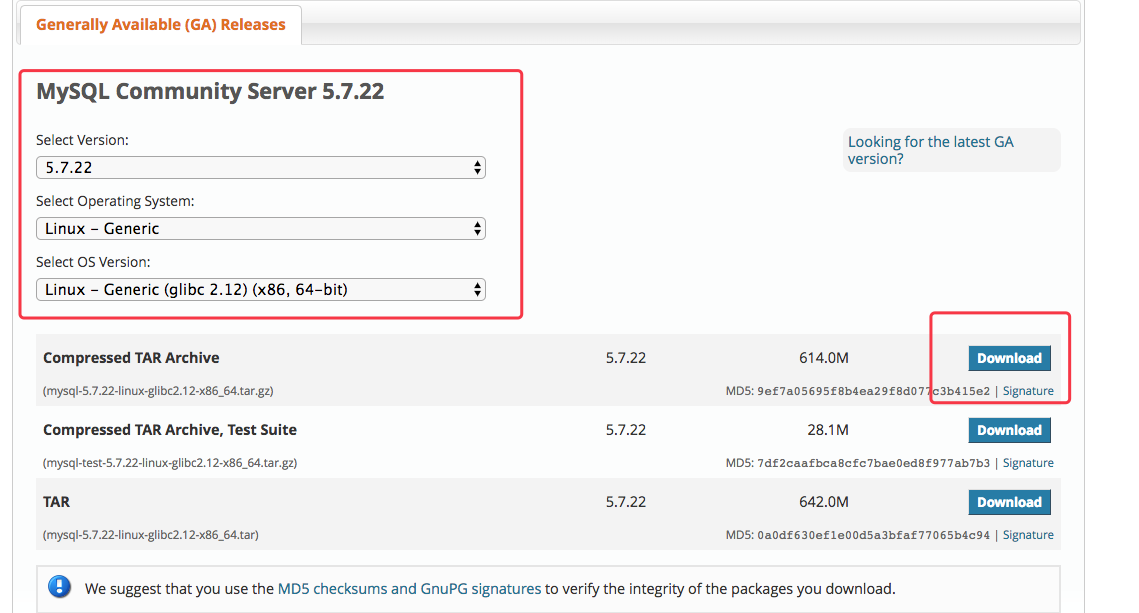
因为 mysql5.7 是没有给一个默认的my.cnf 的,
As of MySQL 5.7.18, my-default.ini is no longer included in or installed by distribution packages.
参考配置: 根据自己的情况修改:
# For advice on how to change settings please see # http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/server-configuration-defaults.html # *** DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE. It‘s a template which will be copied to the # *** default location during install, and will be replaced if you # *** upgrade to a newer version of MySQL. [mysqld] #sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES explicit_defaults_for_timestamp=1 skip-external-locking server_id=1 # 一般配置选项 basedir = /opt/mysql57 datadir = /srv/db/mysql57/data port = 3306 socket = /tmp/mysql.sock key_buffer_size = 384M character-set-server=utf8 max_connections = 3000 #max_connect_errors = 50 # 默认 100 table_open_cache = 4096 max_allowed_packet = 32M #binlog_cache_size = 4M read_rnd_buffer_size = 16M sort_buffer_size = 16M join_buffer_size = 16M thread_cache_size = 16 query_cache_size = 128M query_cache_limit = 4M ft_min_word_len = 8 thread_stack = 512K transaction_isolation = REPEATABLE-READ tmp_table_size = 1024M max_heap_table_size = 1024M log-bin=mysql-bin # expire_logs_days = 60 # binlog 自动清理天数, 即60天之前的binlog 自动删除, 只保留最近60天数据 # log_slave_updates # 从库级联复制, 只有主从时 主->从->从 时才有用 log_slave_updates = 1 binlog_format=mixed # 可选模式 ROW #慢查询sql日志设置 #slow_query_log = 1 #long_query_time = 6 #slow_query_log_file = slow.log #检查未使用到索引的sql # log_queries_not_using_indexes = 1 slow_query_log=1; long_query_time = 10 slow_query_log_file=/srv/logs/mysql/slow-sql.log #针对log_queries_not_using_indexes开启后,记录慢sql的频次、每分钟记录的条数 # log_throttle_queries_not_using_indexes = 5 innodb_buffer_pool_size = 6G #innodb_thread_concurrency = 32 #innodb_thread_concurrency默认是0,则表示没有并发线程数限制,所有请求都会直接请求线程执行。注意:当 innodb_thread_concurrency 设置为0时,则innodb_thread_sleep_delay的设置将会被忽略,不起作用。如果数据库没出现性能问题时,使用默认值即可。 innodb_log_buffer_size = 16M innodb_log_file_size = 1024M innodb_log_files_in_group = 3 innodb_max_dirty_pages_pct = 90 innodb_lock_wait_timeout = 120 # 锁等待时间 120s innodb_file_per_table = on innodb_print_all_deadlocks = on # 强制将死锁语句写入err log 中, 以方便压测监控查看 # other lower_case_table_names = 1 # 是否对sql语句大小写敏感,1表示不敏感 默认: lower_case_table_names | 0 # 临时目录 比如load data infile会用到, 默认 /tmp, 如果你系统盘容量不大, 请更改, 如果系统盘不是ssd 请更改 #tmpdir = /srv/db/mysql57/tmp #在MySQL暂时停止响应新请求之前的短时间内多少个请求可以被存在堆栈中 #官方建议back_log = 50 + (max_connections / 5),封顶数为900 back_log = 300 [mysqldump] quick max_allowed_packet = 32M [mysql] no-auto-rehash default-character-set=utf8 safe-updates [myisamchk] key_buffer = 16M sort_buffer_size = 16M read_buffer = 8M write_buffer = 8M [mysqlhotcopy] interactive-timeout [mysqld_safe] open-files-limit = 8192
thread_pool_oversuscribe 在5.7.22中不可用

mysql5.7 的安装与启动:
安装准备工作:
yum -y install libaio numactl.x86_64
不然可能报错:
./mysqld: error while loading shared libraries: libaio.so.1: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
or
./mysqld: error while loading shared libraries: libnuma.so.1: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
非安全模式安装: 即 root 空密码 ./mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/my57.cnf --initialize-insecure --user=mysql --basedir=/opt/mysql57/ --datadir=/srv/db/mysql57/data 安全模式安装: root自动生成一个密码: ./mysqld --defaults-file=/etc/my57.cnf --initialize --user=mysql --basedir=/opt/mysql57/ --datadir=/srv/db/mysql57/data
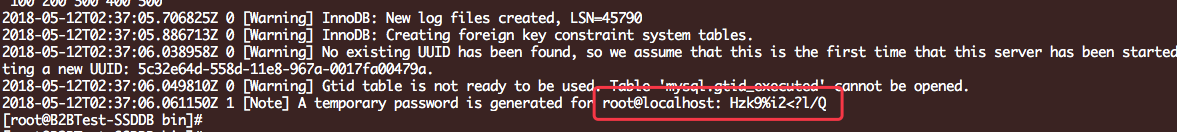
开启mysql服务:
./mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my57.cnf --user=mysql
此时使用密码登录你会发现提示密码过期:

解决方法之一:
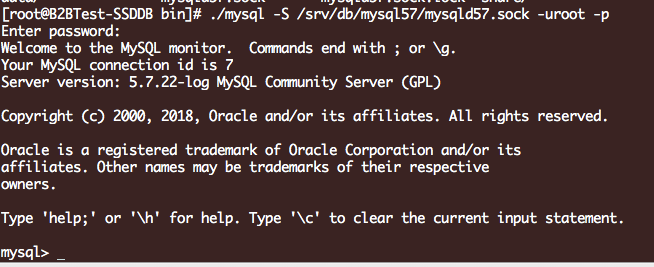
./mysqladmin -S /srv/db/mysql57/mysqld57.sock -uroot -p'Hzk9%i2<?l/Q' password 123456

使用123456登录成功:
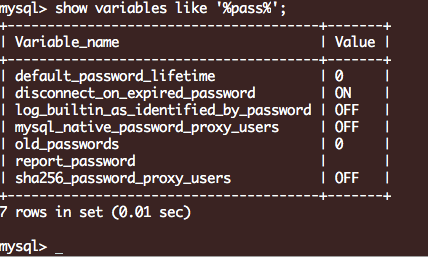
看了下登录密码过期配置也是没有配置的,不知为什么安装 上去就提示密码过期, 也许是为了强调安全的重要吧:
其它方法:
./mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my57.cnf --user=mysql --skip-grant-tables
# 因为刚创建的用户密码就过期 需要手动修改一下过期为永不过期:
update user set password_expired='N' where user='root';
update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('123456') where user='root';
or
ALTER USER USER() IDENTIFIED BY '123456';
or
./mysqladmin -S /srv/db/mysql57/mysqld57.sock -uroot -p123456 password 789
# 重启mysql
./mysqld_safe --defaults-file=/etc/my57.cnf --user=mysql
mysql从5.7.4开始对用户:
[mysqld]
default_password_lifetime=90
如果要设置密码永不过期的全局策略,可以这样:(注意这是默认值,配置文件中可以不声明)
[mysqld]
default_password_lifetime=0
在MySQL 5.7.8版开始用户管理方面添加了锁定/解锁用户账户的新特性
开启密码过期
ALTER USER 'xxx'@'localhost' PASSWORD EXPIRE;
添加帐号过期间隔:
ALTER USER 'xxx'@'localhost' PASSWORD EXPIRE INTERVAL 30 DAY;
锁定帐号:
ALTER USER 'xxx'@'localhost' ACCOUNT LOCK;
解锁帐号:
ALTER USER 'xxx'@'localhost' ACCOUNT UNLOCK;
创建一个锁帐号:
CREATE USER 'xxx'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123' ACCOUNT LOCK;
以下是mysql 启动脚本: 按需修改配置: mysql.server
mysql.server start
mysql.server stop
mysql.server restart
可放到 /etc/init.d/mysqld 文件里, 服务启动 services mysqld start
#!/bin/sh
# Copyright Abandoned 1996 TCX DataKonsult AB & Monty Program KB & Detron HB
# This file is public domain and comes with NO WARRANTY of any kind
# MySQL daemon start/stop script.
# Usually this is put in /etc/init.d (at least on machines SYSV R4 based
# systems) and linked to /etc/rc3.d/S99mysql and /etc/rc0.d/K01mysql.
# When this is done the mysql server will be started when the machine is
# started and shut down when the systems goes down.
# Comments to support chkconfig on RedHat Linux
# chkconfig: 2345 64 36
# description: A very fast and reliable SQL database engine.
# Comments to support LSB init script conventions
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: mysql
# Required-Start: $local_fs $network $remote_fs
# Should-Start: ypbind nscd ldap ntpd xntpd
# Required-Stop: $local_fs $network $remote_fs
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: start and stop MySQL
# Description: MySQL is a very fast and reliable SQL database engine.
### END INIT INFO
# If you install MySQL on some other places than /usr/local/mysql, then you
# have to do one of the following things for this script to work:
#
# - Run this script from within the MySQL installation directory
# - Create a /etc/my.cnf file with the following information:
# [mysqld]
# basedir=<path-to-mysql-installation-directory>
# - Add the above to any other configuration file (for example ~/.my.ini)
# and copy my_print_defaults to /usr/bin
# - Add the path to the mysql-installation-directory to the basedir variable
# below.
#
# If you want to affect other MySQL variables, you should make your changes
# in the /etc/my.cnf, ~/.my.cnf or other MySQL configuration files.
# If you change base dir, you must also change datadir. These may get
# overwritten by settings in the MySQL configuration files.
basedir=/opt/mysql57
datadir=/srv/db/mysql57/data
# Default value, in seconds, afterwhich the script should timeout waiting
# for server start.
# Value here is overriden by value in my.cnf.
# 0 means don't wait at all
# Negative numbers mean to wait indefinitely
service_startup_timeout=900
# Lock directory for RedHat / SuSE.
lockdir='/var/lock/subsys'
lock_file_path="$lockdir/mysql"
# The following variables are only set for letting mysql.server find things.
# Set some defaults
mysqld_pid_file_path=
if test -z "$basedir"
then
basedir=/usr/local/mysql
bindir=/usr/local/mysql/bin
if test -z "$datadir"
then
datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data
fi
sbindir=/usr/local/mysql/bin
libexecdir=/usr/local/mysql/bin
else
bindir="$basedir/bin"
if test -z "$datadir"
then
datadir="$basedir/data"
fi
sbindir="$basedir/sbin"
libexecdir="$basedir/libexec"
fi
# datadir_set is used to determine if datadir was set (and so should be
# *not* set inside of the --basedir= handler.)
datadir_set=
#
# Use LSB init script functions for printing messages, if possible
#
lsb_functions="/lib/lsb/init-functions"
if test -f $lsb_functions ; then
. $lsb_functions
else
log_success_msg()
{
echo " SUCCESS! $@"
}
log_failure_msg()
{
echo " ERROR! $@"
}
fi
PATH="/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin:$basedir/bin"
export PATH
mode=$1 # start or stop
[ $# -ge 1 ] && shift
other_args="$*" # uncommon, but needed when called from an RPM upgrade action
# Expected: "--skip-networking --skip-grant-tables"
# They are not checked here, intentionally, as it is the resposibility
# of the "spec" file author to give correct arguments only.
case `echo "testing\c"`,`echo -n testing` in
*c*,-n*) echo_n= echo_c= ;;
*c*,*) echo_n=-n echo_c= ;;
*) echo_n= echo_c='\c' ;;
esac
parse_server_arguments() {
for arg do
case "$arg" in
--basedir=*) basedir=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'`
bindir="$basedir/bin"
if test -z "$datadir_set"; then
datadir="$basedir/data"
fi
sbindir="$basedir/sbin"
libexecdir="$basedir/libexec"
;;
--datadir=*) datadir=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'`
datadir_set=1
;;
--pid-file=*) mysqld_pid_file_path=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'` ;;
--service-startup-timeout=*) service_startup_timeout=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'` ;;
esac
done
}
wait_for_pid () {
verb="$1" # created | removed
pid="$2" # process ID of the program operating on the pid-file
pid_file_path="$3" # path to the PID file.
i=0
avoid_race_condition="by checking again"
while test $i -ne $service_startup_timeout ; do
case "$verb" in
'created')
# wait for a PID-file to pop into existence.
test -s "$pid_file_path" && i='' && break
;;
'removed')
# wait for this PID-file to disappear
test ! -s "$pid_file_path" && i='' && break
;;
*)
echo "wait_for_pid () usage: wait_for_pid created|removed pid pid_file_path"
exit 1
;;
esac
# if server isn't running, then pid-file will never be updated
if test -n "$pid"; then
if kill -0 "$pid" 2>/dev/null; then
: # the server still runs
else
# The server may have exited between the last pid-file check and now.
if test -n "$avoid_race_condition"; then
avoid_race_condition=""
continue # Check again.
fi
# there's nothing that will affect the file.
log_failure_msg "The server quit without updating PID file ($pid_file_path)."
return 1 # not waiting any more.
fi
fi
echo $echo_n ".$echo_c"
i=`expr $i + 1`
sleep 1
done
if test -z "$i" ; then
log_success_msg
return 0
else
log_failure_msg
return 1
fi
}
# Get arguments from the my.cnf file,
# the only group, which is read from now on is [mysqld]
if test -x "$bindir/my_print_defaults"; then
print_defaults="$bindir/my_print_defaults"
else
# Try to find basedir in /etc/my.cnf
conf=/etc/my.cnf
print_defaults=
if test -r $conf
then
subpat='^[^=]*basedir[^=]*=\(.*\)$'
dirs=`sed -e "/$subpat/!d" -e 's//\1/' $conf`
for d in $dirs
do
d=`echo $d | sed -e 's/[ ]//g'`
if test -x "$d/bin/my_print_defaults"
then
print_defaults="$d/bin/my_print_defaults"
break
fi
done
fi
# Hope it's in the PATH ... but I doubt it
test -z "$print_defaults" && print_defaults="my_print_defaults"
fi
#
# Read defaults file from 'basedir'. If there is no defaults file there
# check if it's in the old (depricated) place (datadir) and read it from there
#
extra_args=""
if test -r "$basedir/my.cnf"
then
extra_args="-e $basedir/my.cnf"
fi
parse_server_arguments `$print_defaults $extra_args mysqld server mysql_server mysql.server`
#
# Set pid file if not given
#
if test -z "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
then
mysqld_pid_file_path=$datadir/`hostname`.pid
else
case "$mysqld_pid_file_path" in
/* ) ;;
* ) mysqld_pid_file_path="$datadir/$mysqld_pid_file_path" ;;
esac
fi
case "$mode" in
'start')
# Start daemon
# Safeguard (relative paths, core dumps..)
cd $basedir
echo $echo_n "Starting MySQL"
if test -x $bindir/mysqld_safe
then
# Give extra arguments to mysqld with the my.cnf file. This script
# may be overwritten at next upgrade.
$bindir/mysqld_safe --datadir="$datadir" --pid-file="$mysqld_pid_file_path" $other_args >/dev/null &
wait_for_pid created "$!" "$mysqld_pid_file_path"; return_value=$?
# Make lock for RedHat / SuSE
if test -w "$lockdir"
then
touch "$lock_file_path"
fi
exit $return_value
else
log_failure_msg "Couldn't find MySQL server ($bindir/mysqld_safe)"
fi
;;
'stop')
# Stop daemon. We use a signal here to avoid having to know the
# root password.
if test -s "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
then
# signal mysqld_safe that it needs to stop
touch "$mysqld_pid_file_path.shutdown"
mysqld_pid=`cat "$mysqld_pid_file_path"`
if (kill -0 $mysqld_pid 2>/dev/null)
then
echo $echo_n "Shutting down MySQL"
kill $mysqld_pid
# mysqld should remove the pid file when it exits, so wait for it.
wait_for_pid removed "$mysqld_pid" "$mysqld_pid_file_path"; return_value=$?
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL server process #$mysqld_pid is not running!"
rm "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
fi
# Delete lock for RedHat / SuSE
if test -f "$lock_file_path"
then
rm -f "$lock_file_path"
fi
exit $return_value
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL server PID file could not be found!"
fi
;;
'restart')
# Stop the service and regardless of whether it was
# running or not, start it again.
if $0 stop $other_args; then
$0 start $other_args
else
log_failure_msg "Failed to stop running server, so refusing to try to start."
exit 1
fi
;;
'reload'|'force-reload')
if test -s "$mysqld_pid_file_path" ; then
read mysqld_pid < "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
kill -HUP $mysqld_pid && log_success_msg "Reloading service MySQL"
touch "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL PID file could not be found!"
exit 1
fi
;;
'status')
# First, check to see if pid file exists
if test -s "$mysqld_pid_file_path" ; then
read mysqld_pid < "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
if kill -0 $mysqld_pid 2>/dev/null ; then
log_success_msg "MySQL running ($mysqld_pid)"
exit 0
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL is not running, but PID file exists"
exit 1
fi
else
# Try to find appropriate mysqld process
mysqld_pid=`pidof $libexecdir/mysqld`
# test if multiple pids exist
pid_count=`echo $mysqld_pid | wc -w`
if test $pid_count -gt 1 ; then
log_failure_msg "Multiple MySQL running but PID file could not be found ($mysqld_pid)"
exit 5
elif test -z $mysqld_pid ; then
if test -f "$lock_file_path" ; then
log_failure_msg "MySQL is not running, but lock file ($lock_file_path) exists"
exit 2
fi
log_failure_msg "MySQL is not running"
exit 3
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL is running but PID file could not be found"
exit 4
fi
fi
;;
*)
# usage
basename=`basename "$0"`
echo "Usage: $basename {start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload|status} [ MySQL server options ]"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0
数据库基准测试:
数据准备 100w数据, 10张表:
sysbench ./tests/include/oltp_legacy/oltp.lua --mysql-host=127.0.0.1 --mysql-user=root --mysql-password=123456 --mysql-port=3307 --mysql-db=test --oltp_tables_count=10 --oltp-table-size=100000 --rand-init=on --threads=1000 --db-driver=mysql prepare
开发压测:
sysbench ./tests/include/oltp_legacy/oltp.lua --mysql-host=127.0.0.1 --mysql-user=root --mysql-password=123456 --mysql-port=3307 --mysql-db=test --oltp_tables_count=10 --oltp-table-size=10 --threads=150 --oltp-read-only=off --report-interval=10 --rand-type=uniform --time=60 --max-requests=0 --percentile=99 --db-driver=mysql run
开启binlog的情况下的测试结果:
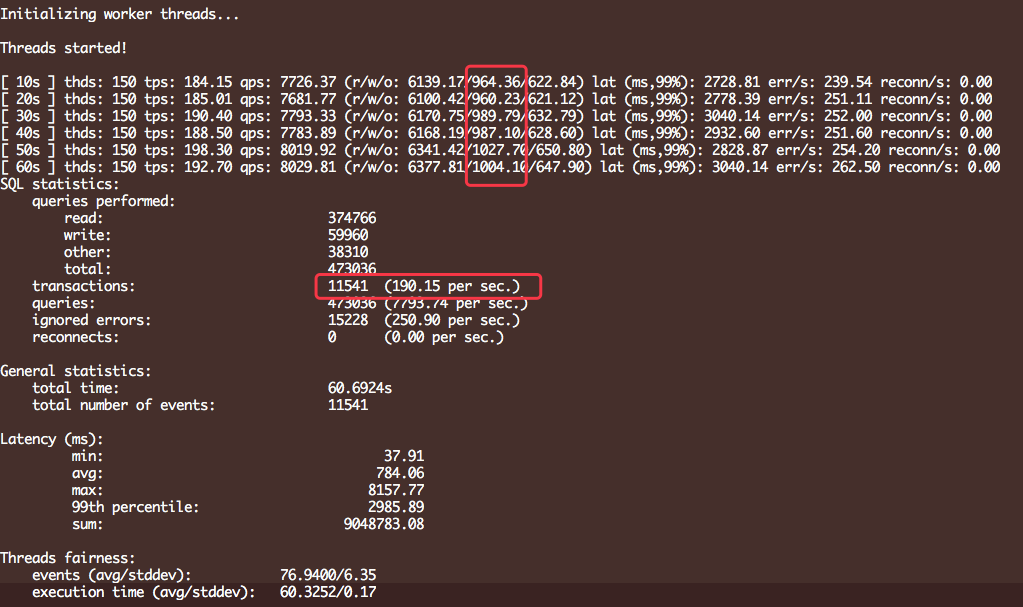
关闭binlog的情况下:
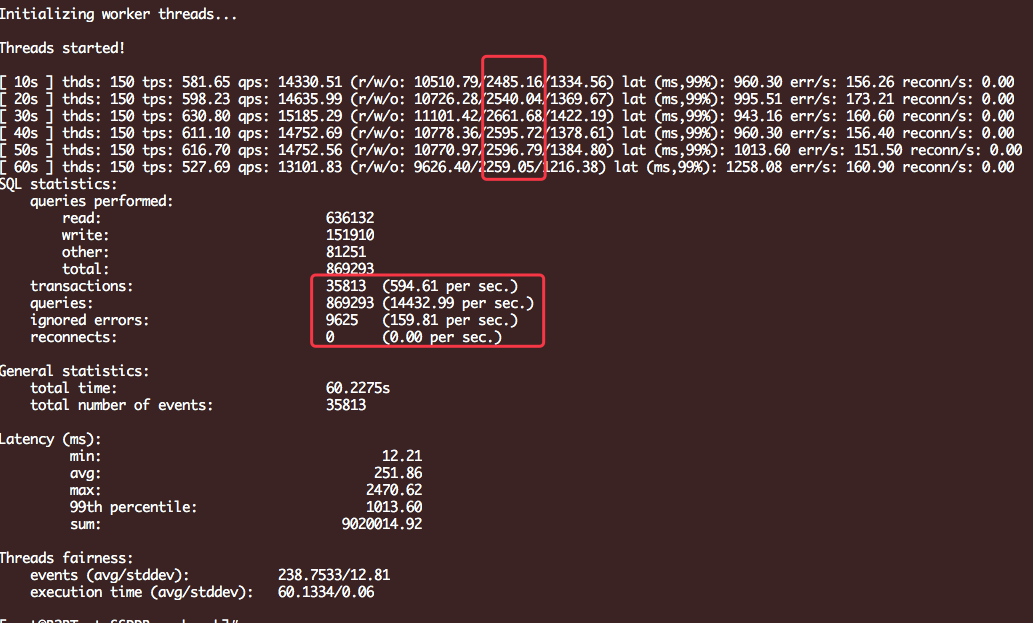
相比较而言还是相差很多的
性能优化:
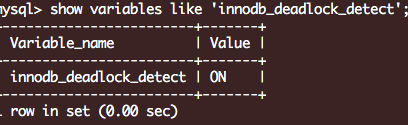
1. 禁止死锁检测后,即使死锁发生,也不会回滚事务,而是全部等待到超时
innodb_deadlock_detect = on
默认开启:
如果关闭: 直接死锁等待:
innodb_deadlock_detect = off
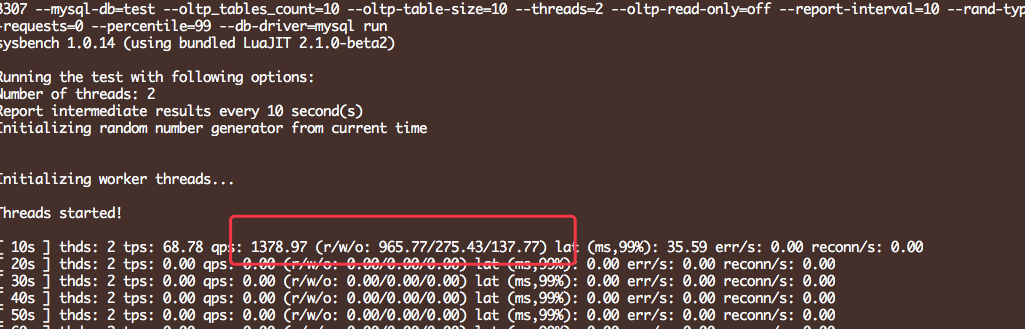
锁状态:
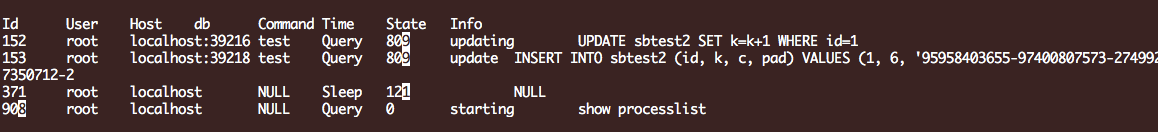
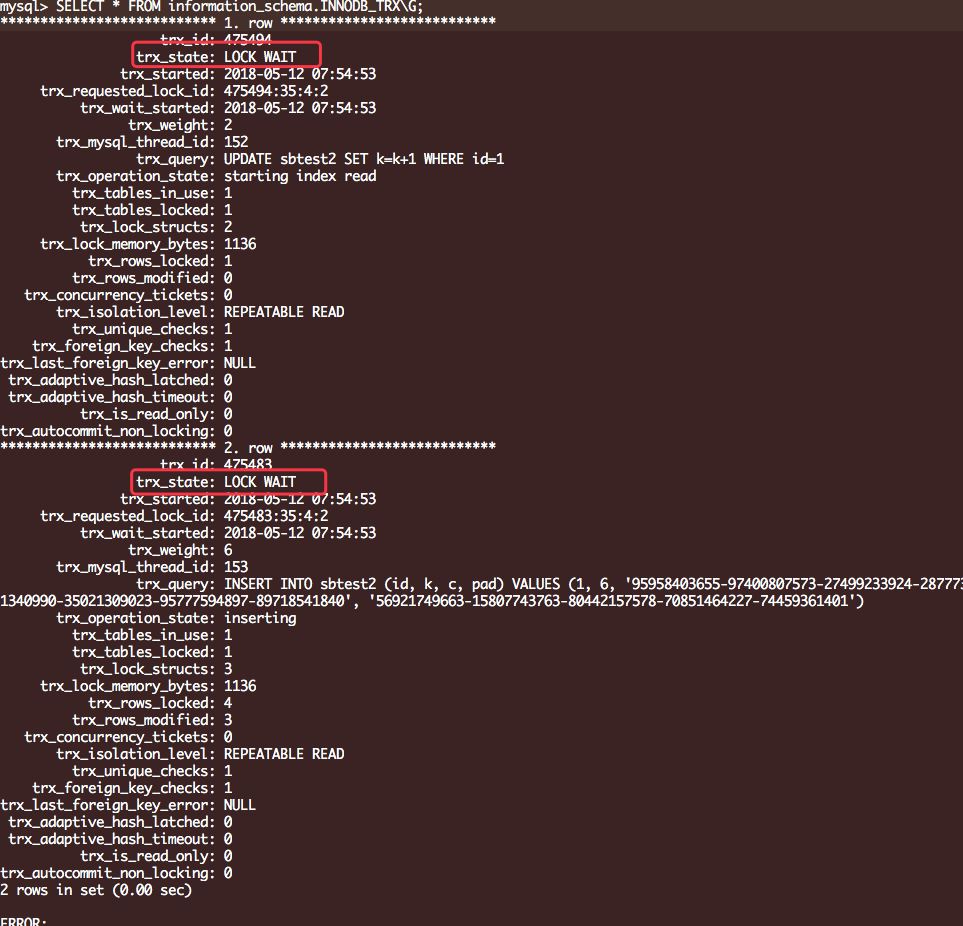
参考脚本:
start.sh
#!/bin/bash echo '例: .sh oltp 172.16.0.11 3306 2' if [ -z $1 ];then echo '请输入测试类型 oltp, select, insert' exit fi if [ -z $2 ];then echo '请输入IP' exit fi if [ -z $3 ];then echo '请输入Mysql 端口号' exit fi if [ -z $4 ];then echo '请输入并发数' exit fi sysbench /srv/sysbench/tests/include/oltp_legacy/$1.lua --mysql-host=$2 --mysql-user=root --mysql-password=123456 --mysql-port=$3 --mysql-db=test --mysql-user=root --mysql-db=test --oltp_tables_count=10 --oltp-table-size=1000000 --threads=$4 --oltp-read-only=off --report-interval=10 --rand-type=uniform --time=600 --max-requests=0 --percentile=99 --db-driver=mysql run
start.bat.sh
#!/bin/bash echo '例: .sh 172.16.0.11 3306 2' if [ -z $1 ];then echo '请输入IP' exit fi if [ -z $2 ];then echo '请输入Mysql 端口号' exit fi if [ -z $3 ];then echo '请输入并发数' exit fi for do_type in "oltp" "select" "insert" do ./start.sh $do_type $1 $2 $3 > $do_type$2$3$4.csv done
压测结果:
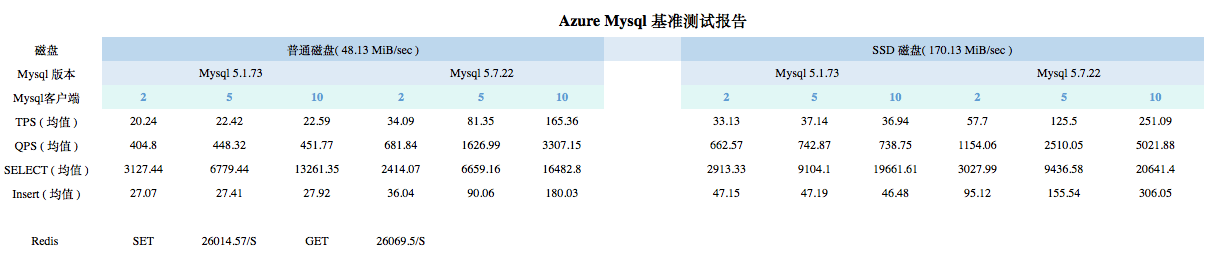
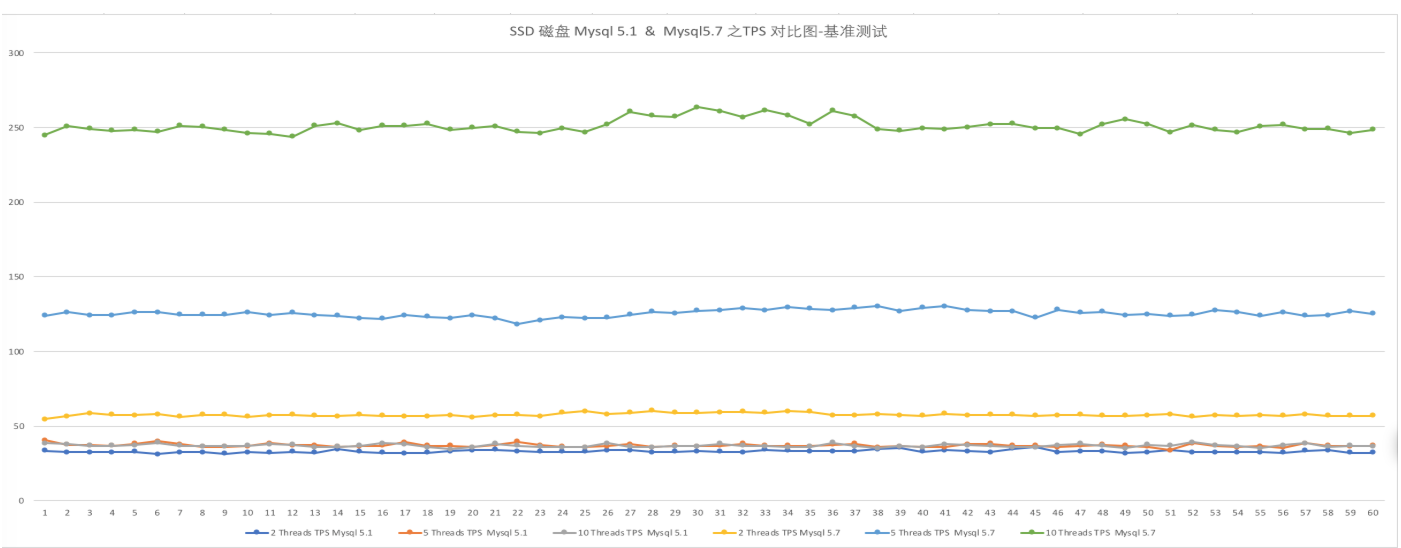
基准测试: 将测试结果 的文件使用excel 生成图表:
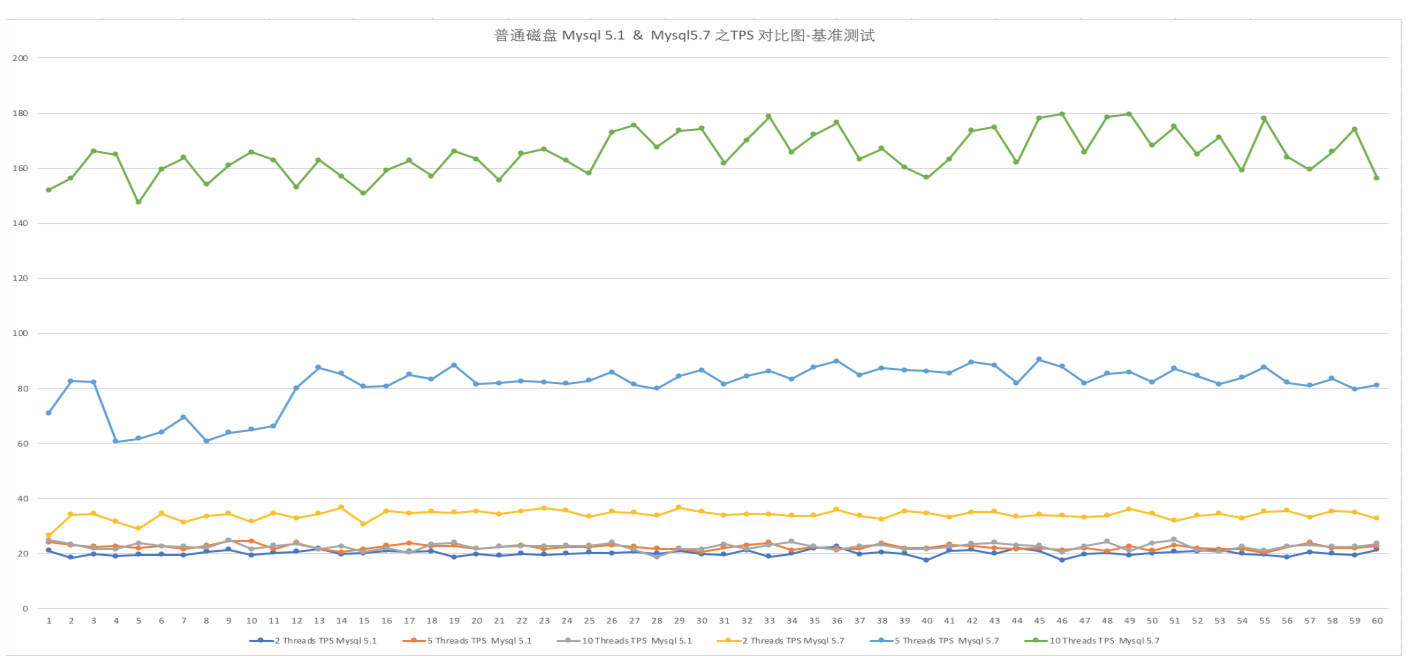
其它相关:
来自: https://blog.csdn.net/bitcarmanlee/article/details/51011515 OLTP和OLAP的区别 联机事务处理OLTP(on-line transaction processing) 主要是执行基本日常的事务处理,比如数据库记录的增删查改。 比如在银行的一笔交易记录,就是一个典型的事务。 OLTP的特点一般有: 1.实时性要求高。我记得之前上大学的时候,银行异地汇款,要隔天才能到账,而现在是分分钟到账的节奏,说明现在银行的实时处理能力大大增强。 2.数据量不是很大,生产库上的数据量一般不会太大,而且会及时做相应的数据处理与转移。 3.交易一般是确定的,比如银行存取款的金额肯定是确定的,所以OLTP是对确定性的数据进行存取 4.高并发,并且要求满足ACID原则。比如两人同时操作一个银行卡账户,比如大型的购物网站秒杀活动时上万的QPS请求。 联机分析处理OLAP(On-Line Analytical Processing) 是数据仓库系统的主要应用,支持复杂的分析操作,侧重决策支持,并且提供直观易懂的查询结果。 典型的应用就是复杂的动态的报表系统。 OLAP的特点一般有: 1.实时性要求不是很高,比如最常见的应用就是天级更新数据,然后出对应的数据报表。 2.数据量大,因为OLAP支持的是动态查询,所以用户也许要通过将很多数据的统计后才能得到想要知道的信息,例如时间序列分析等等,所以处理的数据量很大; 3.OLAP系统的重点是通过数据提供决策支持,所以查询一般都是动态,自定义的。 所以在OLAP中,维度的概念特别重要。一般会将用户所有关心的维度数据,存入对应数据平台。 总结: OLTP即联机事务处理,就是我们经常说的关系数据库,增删查改就是我们经常应用的东西,这是数据库的基础; TPCC(Transaction Processing Performance Council)属于此类。 OLAP即联机分析处理,是数据仓库的核心部心,所谓数据仓库是对于大量已经由OLTP形成的数据的一种分析型的数据库,用于处理商业智能、决策支持等重要的决策信息; 数据仓库是在数据库应用到一定程序之后而对历史数据的加工与分析,读取较多,更新较少,TPCH属于此类。 随着大数据时代的到来,对于OLAP, 列存储模式或者说nosql模式比传统意义的行存储模式可能更具优势。